���¼��ʹ�ô˹��ܡ�
������ʹ�ô˹��ܽ���Ʒ���ӵ������ղ��б���
�ر�
�����ղ��б���ɾ������Ʒ��
�ر�
���¼��ʹ�ô˹��ܡ�
������ʹ�ô˹��ܽ���˾���ӵ������ղؼ��б���
�ر�
��ҹ�˾�Ѵ�����ղؼ��б���ɾ����
�ر�
���¼��ʹ�ô˹��ܡ�
������ʹ�ô˹��ܽ���˾���ӵ�����ѯ�ʳ���
�ر�
��ҹ�˾�ѱ����ӵ�����ѯ�ʳ���
�ر�
����Ʒ�ѱ����ӵ�����ѯ�ʳ���
�ر�
����Ʒ�Ѿ�������ѯ�۳���ɾ����
�ر�
��Ʒ/��˾�Ѵﵽ������ѯ�۳���������
�ر�
�����ղ��б���ɾ������Ʒ��
�ر�
ÿ�յ�¼����
��ϲ!
�����˽����ÿ�յ�¼������
5 NP Point��������õĽ�����
�鿴����ÿ�յ�¼����
ȷ��ÿ����������Ի����Ľ�����
лл��
Scan and Whatsapp Me
![qr code]() Note: Some mobile phone default QR scanners cannot scan to open the WhatsApp App directly.
Cancel
Note: Some mobile phone default QR scanners cannot scan to open the WhatsApp App directly.
Cancel
Ӫҵ
ʱ��
����һ - ������ 8:30 AM - 5:30 PM
������ 9:00 AM - 12:30 PM
������ ��Ϣ
������
����������Ϣ
Ӫҵ
��Ϣ
Linear Shaft vs Linear Rails - WHEELER MECTRADE (S) PTE LTD
Linear Shaft vs Linear Rails
07-Dec-2023
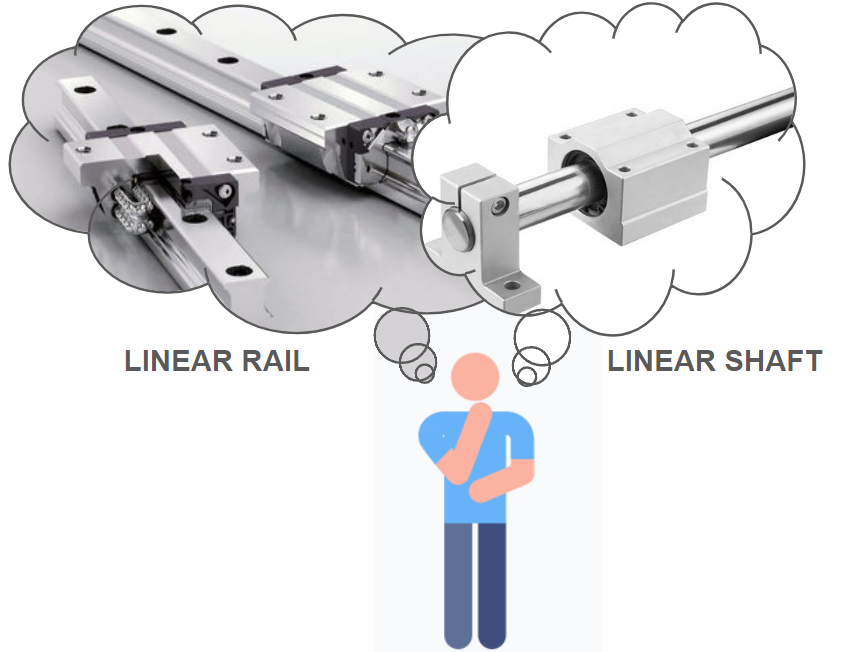
Both linear shafts and linear rails are used for linear motion, but there are some key differences between them:
Linear shafts:
-
Simple design: A round shaft made of steel, stainless steel, or hardened chrome.
-
Lower cost: Generally cheaper than linear rails.
-
Easy to install: Can be supported by bearings or bushings.
-
Less accurate: Can bend or deflect under load, leading to less precise motion.
-
Lower load capacity: Not suitable for high-load applications.
-
Higher friction: Requires more lubrication than linear rails.
-
Limited self-alignment: Can twist or rotate under load, requiring additional components to prevent it.
Linear rails:
-
More complex design: Consists of a hardened steel rail with rolling elements like ball bearings or rollers.
-
Higher cost: More expensive than linear shafts.
-
More difficult to install: Requires precise alignment and mounting.
-
More accurate: Offers more precise and consistent motion due to its rigid design.
-
Higher load capacity: Can handle heavier loads than linear shafts.
-
Lower friction: Requires less lubrication than linear shafts.
-
Self-aligning: Some types of linear rails can self-align, compensating for minor misalignment.
Key differences:
|
Feature |
Linear shaft |
Linear rail |
|
Design |
Simple, round shaft |
Complex, with rolling elements |
|
Cost |
Lower |
Higher |
|
Installation |
Easy |
Difficult |
|
Accuracy |
Lower |
Higher |
|
Load capacity |
Lower |
Higher |
|
Friction |
Higher |
Lower |
|
Self-alignment |
Limited |
Some types |
Choosing between linear shafts and linear rails:
The best choice for your application will depend on several factors, including:
-
Required level of accuracy and precision
-
Expected load
-
Budget
-
Complexity of installation
-
Need for self-alignment
Here are some general guidelines:
-
Use linear shafts for:
-
Low-cost applications
-
Simple designs
-
Light loads
-
Non-critical applications where high accuracy is not required
-
Use linear rails for:
-
High-precision applications
-
Heavy loads
-
Complex designs
-
Applications requiring self-alignment
Here are some additional resources that you may find helpful:





 US 8850
US 8850  GB 6359
GB 6359  CA 5462
CA 5462  AU 5439
AU 5439  IE 2993
IE 2993  NZ 2831
NZ 2831  IN 721
IN 721  SG 569
SG 569 



